
Residential IP, Data Center IP(Hosting IP )Introduction
Residential IP
A residential IP is an IP address assigned to home users. They are allocated by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to households or individual users.
Since residential IPs originate from real home networks, users with residential IPs are generally considered genuine users.
However, residential IPs have disadvantages in terms of stability, bandwidth, and speed compared to data center IPs.
Data Center IP or Hosting IP:
A data center IP is an IP address assigned to servers located in data centers. These servers are typically used for hosting enterprise applications, websites, cloud computing, big data processing, and other services.
Data center IPs, being located in data centers, generally offer higher stability, bandwidth, and speed.
How to determine whether it is a residential IP or a data center IP?
We can use third-party websites such as https://ipinfo.io to determine whether an IP is a residential IP or a data center IP.
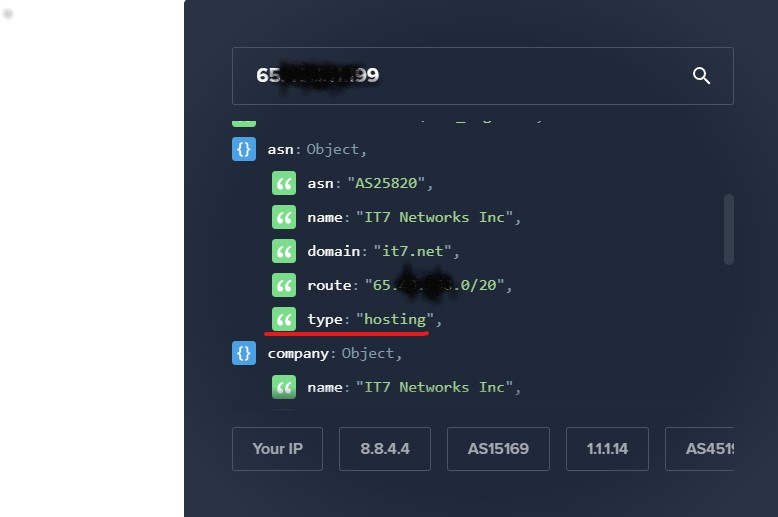
By entering the IP address and checking the “asn type” information, if it is labeled as “isp,” it represents a residential IP, while “hosting” indicates a data center IP.
Relationship between Residential IP, Data Center IP, and Native IP?
Residential IP and data center IP are mutually exclusive concepts, but they are not related to native IP. A native IP can be either a residential IP or a data center IP.
A native IP refers to an IP address where the country of the IP’s ISP matches the geographical location of the server. For detailed information on native IP, please refer to: How to determine native IP?